Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Structure, and Characteristics
About Course
You must be logged in to view this content.
Course Content
Eukaryotic Cells
-
Eukaryotic cells
-
What Are Eukaryotic Cells?
-
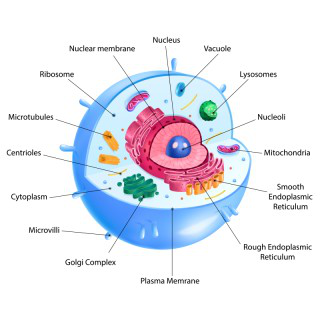
The main parts of a cell
-
Parts of a Cell
-
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
-
Eukaryotic Cells – Definition, Structure, and Characteristics
Student Ratings & Reviews

No Review Yet
